The Chinese Academy of Social Sciences and UN-HABITAT jointly released the 《Global Urban Competitiveness Report 2019-2020 -The world: 300 years of transformation into city》
The annual general report examines the global 300-year change from the perspective of cities and finds that from 1750 to 2050, the world of 300 years will completely enter the city.
The annual theme report identifies municipal financing challenges and systematically summarizes “Experience and Methods of Global Municipal Finance”.
The annual competitiveness report found that the average value of global urban competitiveness declined slightly due to the decline in the competitiveness of Chinese, American and European cities.
The annual report puts forward a set of standards for city classification for the first time, and adopts hierarchical clustering method to classify more than1,000 cities all around the world.
The annual report attempts to measure the progress of the implementation of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) from the perspective of Urban Sustainable Competitiveness (USC) for the first time.
On November 12, 2019, the China Social Science Forum - Global Urban Forum was held in Ningbo. The meeting was co-organized by the Presidium of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences(CASS), UN-HABITAT and the Municipal People's Government of Ningbo, and undertaken by National Academy of Economic Strategy, CASS, along with the Government of Yinzhou District . The forum is also supported by "Economic Daily", "South China Morning Post", Phoenix Finance,.etc. World-renowned scholars from UN-HABITAT and CASS, entrepreneurs, government officials and media leaders attended and delivered keynote speeches, theme speeches and made dialogues on new type city, municipal finance, and media to enhance urban influence.
At the forum, The Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (National Academy of Economic Strategy) and UN-HABITAT jointly released the 《Global Urban Competitiveness Report 2019-2020 - The world: 300 years of transformation into city 》(hereinafter referred to as the report). Led by Mr. Marco Kamiya (UN-HABITAT Head Urban Economy and Finance branch, Co-chief economist of CASS & UN-HABITAT joint research group) and Prof. Ni PengFei (Dean assistant of National Academy of Economic Strategy, Co-chief economist of CASS & UN-HABITAT joint research group), the report is prepared by many urban experts and professionals and lasted for a whole year to complete. This report authorizes the global premier to the English abstract of the "South China Morning Post", the Chinese abstract of the “Daily Economy”, and the live broadcast to the Phoenix Finance.

The annual general report examines the global 300-year change from the perspective of cities and found that from the micro level, the change of leading cities causes the basic "cell" change of the world. There are three notable changes in this process: First is the change in the content of production, exchange and distribution activities in leading cities from goods to services and ideological products. The second is the change in the population size of leading cities from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands and millions. Third is the space of leading cities spread from single central cities to multi-center metropolitan areas, and then to continuous urban clusters. Leading cities not only bring the world into the city, but also change the city world.
Secondly, from the perspective of macro structure, the evolution of the global urban system determines the transformation of the world structure and system. First is the evolution of urban economic system: from global duality to global integration, from commodity trading system to factor trading system, and then from industrial chain system to innovation chain system. Second is the evolution of urban scale system: from the system dominated by small cities in Europe and America to the system dominated by big cities all over the world. Third is the evolution of urban space system: from isolated city to urban agglomeration and then to the world of metropolitan area.The transformation of the global urban system has leaded to the content upgrading and spatial remodeling of world system.
Thirdly, from the perspective of macro gross, the general report found that global urban development has completed the epoch-making transformation of human civilization. Urban economy in the overall economy plays roles from insignificant subsidiary, to pivotal support, and then to all-inclusive main body.Second, the proportion of urban population is about to increase from 5.5% (1750) to 70% (2050). Thirdly, The functional space of the city on earth ranges from scattered points to all human footprints.
Fourthly,from the perspective of space, the general report found that changes in global urban characteristics determine the evolution of world characteristics. First, cities lead the world: from dispersed-concentration to concentrated -concentration and then to concentrated-dispersion. Secondly, cities dominate the world: from regional connections to global connections, from “hard connections” of commodity elements to “soft connections” of information and service elements, from individual connections to the internet of everything, from infrastructure contribution to public service contribution, from hardware product sharing to software product sharing, from public product sharing to private product sharing. The three important characteristics of human society: aggregation, connection and sharing are accelerated by the development of cities.
Last but not least, from the dynamic mechanism, the general report found that the human development momentum bred by cities determines the appearance and change of the urban world. Mankind's insatiable and ever-escalating demand for a better life is the driving force behind the urbanization of the world in 300 years. The four technological revolutions have been the core driving force behind 300 years of urban world formation. The establishment and expansion of market economy system is the key driving force of urban world.
According to the theme report, the serious challenges of municipal financing and solutions need to be given high attention globally. Municipalities are the government entities that most closely manage cities, and are well situated to respond to the specific needs of their resident populations and businesses in terms of public services, education, an enabling business environment and governance impacting the local quality of life. However, lack of resources, capacity and authority often constrains the ability of municipalities to meet the needs of their cities. Therefore, improving the state of municipal finance will be critical for development, and is a global priority according to the Addis Ababa Action Agenda (United Nations, 2015B).
The theme report found that SDGs cannot be achieved without determined and far-reaching financial efforts in terms of capital investment. Thus, cities must concentrate a significant part of these efforts. However the expenditure and funding raising ability of local governments shown significant differences between high-income and low-income cities. Therefore, innovation in resource access mechanisms is essential.
The case study part of the theme report, centering on the experience and methods of municipal finance, deeply analyzes the cases of Sao Paulo, Botswana, and Latin America and the Caribbean, summarizes the experience and practices of these cities and regions in municipal finance so as to provide references for global urban.
Using a sound theoretical framework and indicator system, official statistical data, big data, and related calculation methods, the report measures the economic competitiveness of 1,006 cities (metropolitan areas) around the world, as well as their constituent indexes, rankings, and changes. The report shows that influenced by the decline in the average urban competitiveness of China, the United States and Europe, the average global urban competitiveness slightly declined. This also indicates that if the trade war between major countries continues, it will not only weaken the urban competitiveness of each country, but also weaken the global urban competitiveness and welfare.
According to the global urban economic competitiveness research, the top 20 cities in the 2019 Global Urban Economic Competitiveness ranking are: New York, London, Singapore, Shenzhen, San Jose, Tokyo, San Francisco, Munich, Los Angeles, Shanghai, Dallas, Houston, Hong Kong, Dublin, Seoul, Boston, Beijing, Guangzhou, Miami and Chicago. Nine of them were from North America, eight from Asia and three from Western Europe.Overall, the top 20 cities face fierce competition with significant changes in rankings. 14 cities has changed position with the largest change of 4 places. Global comprehensive centers and technology centers have generally improved, while specialized cities and manufacturing centers declined overall.
The study found that comparing the top200 cities in economic competitiveness, Europe has more cities declined in the ranking while Asia has more cities improved. Compared with 2018, among the top200 cities, 54.2% of European cities declined in terms of ranking of economic competitiveness while this ratio in Asia is only 31% which indicates that the majority of cities in Asia are improved in the ranking. Regarding North America, the number of risen is as much as fallen.
The study found that among the top ten urban agglomerations, Northern California has the highest average and Rhein-Ruhr has the smallest internal difference. The study found that the economic competitiveness of the top ten urban agglomerations showed a trend of increasing differentiation. The ranks of the Northern California urban agglomerations have risen significantly and the Seoul metropolitan area, the Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Delta have also improved in but with smaller extent. The Northeastern US urban agglomeration, the Midwestern urban agglomeration, the London-Liverpool urban agglomeration, the Netherlands The Belgian urban agglomeration and the Rhine-Ruhr urban agglomerations have declined slightly . The overall ranking of the Mumbai urban agglomeration is relatively low but stable.
Comparing the three major economies of China, the United States and the European Union, China has more cities declined in the ranking, while some European cities have declined steeply . As the three engines of world economic development, China, the United States and the European Union have attracted worldwide attention for the change of urban economic power. From the perspective of urban economic competitiveness, the overall level of the three major economies has declined. The United States has the smallest number of cities declined and China has the biggest number but with slight overall descent degree. However, severity declines have appear in some European cities.
Comparing the overall pattern of global economic competitiveness, the report found that the overall level has declined, but the divergence has narrowed. Comparing all 1006 samples, it is found that compared with 2018, the average level of global urban economic competitiveness in 2019 has decreased, but the difference has converged. Meanwhile, from the perspective of spatial distribution, the cities with better economic competitiveness output are still mainly concentrated in Western Europe and North America, while the number and scale of cities with strong economic competitiveness in east Asia are smaller. From the aspect of urban competitiveness upgrading, European and African cities present more growth than decrease, while Asian and north American cities present more decrease than growth.
Comparing changes of global sub-regional pattern, the report found that Northern China and Eastern Europe declined while Southern China and India rose in ranking. From the perspective of spatial distribution, the cities with rising global competitiveness are mainly distributed in the west coast of the United States (100 degrees west longitude), Western Europe (20 degrees east longitude) and China, Japan and South Korea (110-140 degrees east longitude), and the latitude is concentrated between north 25 to north 55 degrees. Cities in Northern China and Eastern Europe generally declined while those in southern China and India generally rose in ranking.
From the perspective of Chinese cities: the number of city declined is over the number of city increased and the average value has decreased. The Matthew effect of specific ranking is significant. However, from the perspective of index, the overall level has declined while the overall gap has narrowed. In terms of regions, there are more cities increased in Eastern China and Central China while the rest parts have the opposite situation.
According to the Global Urban Competitiveness Report 2019, five cities in China rank among the top 20, namely Shenzhen No. 4, Shanghai No. 10, Hong Kong No. 13, Beijing No. 17, and Guangzhou No. 18. Compared with 2018, Shanghai has increased by 3, Beijing has increased by 2, Hong kong has decreased by 2, and Guangzhou has decreased by 4. Shanghai surpasses Hong Kong.
Nine cities in China have entered the top 50, including Suzhou (25), Nanjing (42), Wuhan (43), and Taipei (44). Compared with the ranking in 2018, Nanjing has increased by 3, Suzhou and Taipei have increased by 2.
Twenty cities in China have entered the top 100, including Chengdu (54), Hangzhou (64), Wuxi (65), Changsha (68), Qingdao (76), Chongqing (81), Tianjin (82), Foshan (84), Ningbo (90), Zhengzhou(94) and Changzhou(99). Ningbo has increased by 11, Hangzhou by 10, Qingdao and Foshan by 9, Changzhou by 8, Chengdu by 6 , Zhengzhou by 5, Changsha by 3 and Tianjin has decreased by 40.
Thirty-nine cities in China have entered the top 200, including: Dongguan (104), Macao (113), Nantong (121), Kaohsiung (126), Ji’nan (141), Hefei (145), Quanzhou (148), Xiamen (149 ), Xi'an (150), Fuzhou (153), Yangzhou (163), Zhuhai (173), Zhenjiang (174), Yantai (175), Taizhou (180), Dalian (185), Xuzhou (191), Nanchang (197) ) and Shenyang (200). Compared with the ranking of 2018, Taizhou has increased by 38, Xi'an by 21, Fuzhou by 20, Dongguan by 20, Yangzhou by 19, Jinan by 16, Zhuhai by 14 and Quanzhou by11. Four cities, including Nantong and Nanchang, have increased by eight, and Chongqing and Xuzhou both have increased by one. Xiamen and Zhenjiang both have decreased by six, Yantai has decreased by nine, Shenyang has decreased by 30, and Dalian has decreased by 60.
According to the 2019 global urban economic competitiveness ranking, for China, there are more cities declined. By regions, in Eastern and Central China, there are more cities increased than decreased but in underdeveloped Western China and resource-based Northeastern regions, there are more cities decreased than increased. In 2019, 103 out of 291 cities in China have increased in terms of economic competitiveness, accounting for 35.4% of the total number. And 182 out of 291 cities have decreased, accounting for 62.54% of the total number.
In 2019, the overall urban economic competitiveness of China is in a middle level, with the mean value
declined slightly and the gap narrowed. In 2019, the mean value of economic competitiveness of 291 cities in China is 0.291, lower than that of 2018 (0.328), and close to the global average (0.292). In 2019, the variance of economic competitiveness level of 291 cities in China is 0.134, slightly lower than that of the last year (0.148) and the variance of the world (0.166). In 2019, the coefficient of variation of economic competitiveness of 291 cities in China is 0.449, slightly lower than that of 0.451 in 2018 and 0.568 of the world.
Using a sound theoretical framework and indicator system, official statistical data, big data, and related calculation methods, the report measures the sustainable competitiveness of 1,006 cities (metropolitan areas) around the world, as well as their constituent indexes, rankings, and changes. The report shows that North American and Western European cities perform well with small divergence, while Asian cities stay in low level with significance difference. Specific as follows:
According to the global urban sustainable competitiveness research, The top 20 cities in 2019 Global Urban Sustainable Competitiveness ranking are Singapore, Tokyo, New York, London, San Francisco, Paris, Hong Kong, Osaka, Los Angeles, Chicago, Barcelona, Moscow, Stockholm, Seoul, Munich, Stuttgart, Boston, Madrid, Shenzhen, and Frankfurt. It basically covers the major cities in the world and the center cities in the developed countries. There are five in U.S., nice in Europe, and the rest are in East Asia, including China, Japan, South Korea and Singapore. Among the top 20 cities, Europe holds the most seats, while Asia has the highest mean value.It is not difficult to find that all the top 20 cities almost represent the characteristics and development of their countries. These leading cities can be regarded as the symbol of the development and achievements of the whole country.
In terms of the top 200 cities, Asia holds the most seats and Europe has the highest mean value. Among the top 200 cities in the 2019 Global Urban Sustainable Competitiveness ranking, Asia has the largest number of cities, namely 65, indicating that Asia is fast growing with a strong upward trend. But we could also find that the average value of Asian cities is low, indicating that their sustainable competitiveness needs to be further improved. Northern America and Europe followed closely, with 60 cities and 58 cities respectively entering the top 200.The mean value of sustainable competitiveness of European cities is the highest, which indicates that the quality of urban development is worthy of recognition.
Comparing the ten largest urban agglomerations, the report found that Seoul has the highest mean value and Rhine-Ruhr is best balanced. Among the ten largest urban agglomerations, the strength of urban agglomerations in the United States and the United Kingdom is prominent. Although urban agglomerations in China, India and other developing countries are large in size, the gap between central cities and surrounding cities is obvious and the development is unbalanced. Due to the limited number of cities in Seoul city cluster, the average sustainable competitiveness index is in a leading position. And among the urban agglomeration in Europe, the Rhine-Ruhr urban agglomeration has the lowest standard deviation, which shows the balance of development in the Western European countries.
The report found that for three major economies: China, the United States and the European Union, the United States and the European Union far surpass China, and the development of US cities is of potential. In total, there are 439 cities in China, the EU and the US entered the global urban competitiveness ranking, which is close to half of the total number of 1006 cities. The overall performances of the EU and the US are in the same level while there is still a large gap for China to catch up. In the US-EU comparison, the United States has a higher cumulative average, indicating that the development potential of American cities is greater than that of Europe. In general, the sustainable competitiveness of Chinese cities has not yet reached the optimal level, and the US and EU cities are at the peak.
According to the report, in terms of the overall global spatial pattern, Northern American and Western European cities perform well with small divergence, while Asian cities stay in low level with significance internal difference. In terms of the global distribution,the average value of North America and Europe is much higher than the world average, and they are at the top of the global sustainable competitiveness with small internal differences. Asia is far ahead of the rest of the continent in terms of the number of cities, but the average value is slightly behind the world average and there are big internal differences. But it is also a sign of the rapid rise of central Asian sub-hubs.
From the perspective of global sub-regional spatial pattern, it shows that coastal cities and cities located in temperate zone are leading. Through the study, we find that the cities with strong sustainable competitiveness are mainly distributed in the coastal areas in the north temperate zone: 120-70 degrees west longitude (east and west coasts of the United States), 10 degrees east longitude to 10 degree west longitude (western European countries) and 110-140 degrees east longitude (China, Japan and South Korea). At the same time, in latitude, the top cities in these areas are mostly between 25 and 55 degrees north latitude.
From the perspective of Chinese cities, the mean value of sustainable competitiveness is close to the world average, and balanced degree surpasses the global average. The sustainable competitiveness of Chinese cities has been steadily improving for many years. According to the data in 2019, there are 2 cities in China ranking top 20, which is Hong Kong (No.7) and Shenzhen(No.19). Among the top 50 cities, Taipei ranks No.23 , Shanghai ranks No.29 , and Beijing ranks No.38. And there are 9 cities enter the top 100 , including Suzhou (58), Guangzhou (67), Nanjing (83), and Xiamen (94). 31 cities enter the top 200, including Wuxi (103), Tianjin (108), Foshan (109), Taizhong (110), Dongguan (121), Wuhan (122), Kaohsiung (124), Hangzhou (130), Chengdu (143), Qingdao (144), Macao (146), Zhongshan (149), Ningbo (154), Changzhou (158), Zhengzhou (159), Tai’nan (164), Changsha (165), Shenyang (182), Zhuhai (189), Dalian (193), Xi'an (197), and Hefei (199).
The sustainable competitiveness of Chinese cities is close to the world average level, and the internal differences are relatively small. The mean value of Chinese cities is 0.333, and the global average is 0.35. China's standard deviation is 0.12, and the global level is 0.17, indicating that Chinese cities, in terms of sustainable competitiveness, are relatively more balanced.
Ningbo has performed well in global competitiveness as its economic competitiveness ranked No.90 in the world in 2019. It is the first time that Ningbo has entered the top 100 most competitive ranking, increased by 11 compared to last year. Among the top 100 cities in the world, ranked No.1 in terms of ranking improvement among Chinese cities. And its sustainable competitiveness ranks No.154 in the world which is relatively of competitive.
For the first time, the report introduces the CASS and UN-HABITAT global urban classification standards . According to the report, urban classification is an important issue of global concern, and new contents and trends have emerged in the global urban development. There are four major innovations in the report: Firstly, from the perspective of elasticity of substitution and based on the theory of spatial economics, a more general economic theoretical framework based on the degree of aggregation and connection of cities is proposed. Secondly, considering the key characteristics of cities of aggregating and connecting, the framework of classification including both degree of aggregation and degree of connection is proposed, and the corresponding index system is designed. Thirdly, considering the major changes in the connotation of the urban world in the era of intelligence, we have re-examined the increasingly important soft elements and products since the origin of the city, and considered the invisible “soft” factors and tangible “hard” factors in the global urban classification framework. Fourth, considering the major changes of cities and their functional systems in the information age, besides traditional financial factors, factors of technological innovation are also emphasized when selecting the indicators of.
According to the theoretical framework, the report establishes the index system, uses the official statistical data and crawler big data, and adopts the hierarchical clustering method to cluster the central index of 1006 sample cities. According to the result, the global urban is divided into 3 layers, 2 categories, 5 groups, and 10 levels : A+,A,B+, B, C+, C, D+, D, E+, E. The first category is strong international cities and the second category is weak international cities. The first group is the global city (A), the second group is the international hub city (B); the third group is the international gateway city (C); the fourth group is the regional hub city (D); the fifth is the regional gateway city ( E).
Global Urban Classification
|
City Level |
Level |
Number |
Mean |
StDev |
C·V |
|
|
Global City (A) |
A+ |
3 |
0.9635 |
0.0320 |
0.0332 |
|
|
A |
2 |
0.9052 |
0.0006 |
0.0006 |
||
|
International Hub City (B) |
B+ |
3 |
0.7585 |
0.0178 |
0.0234 |
|
|
B |
26 |
0.6423 |
0.0464 |
0.0723 |
||
|
International Gateway City (C) |
C+ |
29 |
0.5322 |
0.0251 |
0.0471 |
|
|
C |
96 |
0.4185 |
0.0354 |
0.0845 |
||
|
Regional Hub City (D) |
D+ |
122 |
0.3269 |
0.0181 |
0.0553 |
|
|
D |
266 |
0.2429 |
0.0244 |
0.1003 |
||
|
Regional Gateway City (E) |
E+ |
389 |
0.1769 |
0.1900 |
0.1072 |
|
|
E |
70 |
0.0776 |
0.0404 |
0.5208 |
||
|
Total |
|
1006 |
0.2565 |
0.1327 |
0.5172 |
|
Specifically, there are 3 cities of A+ level, New York, London and Tokyo; 2 cities of A level, including Beijing and Paris which shows that the global urban system is undergoing important changes, and Chinese cities have become an important pole in the world ; as international hubs, there are 3 B+ level cities, including Seoul, Shanghai and Chicago; 26 cities of B level, mainly including Singapore, Hong Kong, Sydney, Dublin,Munich,Toronto,Osaka,etc; as international gateways, there are 29 cities of C+ level, mainly including Melbourne, Buenos Aires, Dubai and Warsaw,Copenhagen,etc.
From the perspective of the intercontinental distribution of cities of different levels, there are obvious differences between the north hemisphere and the south hemisphere in the global city system, and the north hemisphere still has an absolute advantage; from the perspective of the national distribution of cities of different levels, the cities of developed countries still have an leading position in the global city system, but the cities of developing countries represented by China and India are rising rapidly. From the perspective of global city distribution of agglomeration - connection, most of the cities in the global city system belong to the type of low agglomeration - low connection. The degree of agglomeration is more important than the degree of connection in determining the level of a city. From the perspective of global city distribution of softness - hardness, most cities in the global city system belong to the type of weak hardness - weak softness, and the role of soft factor is more important than hard factor in determining the city level.
Beijing is the only city of developing country in the world with the highest grade A, but other Chinese cities are distributed in varying levels. As a Global City, Beijing ranks 4 in the city level score, 5 in agglomeration degree and 2 in connection degree, and Beijing has more advantages in connection degree. Among them, Beijing ranks 2 in hard connection degree and 4 in soft connection degree, which shows that Beijing has absolute advantages in hard connection degree.
Shanghai has advantages in hard connection and disadvantages in soft connection. There are only 3 B+ cities in the world, with Shanghai occupying 1 seat. As an international hub city, Shanghai ranks 7 in the city level score, with 9 in agglomeration degree and 8 in connection degree, indicating that Shanghai has an advantage in connection degree. The ranking of soft connection degree and hard connection degree is 27 and 7 respectively, which shows that Shanghai has advantages in hard connection degree and disadvantages in soft connection degree.
Hong Kong and Taipei have advantages in hard agglomeration and disadvantages in weak connection. Chinese Hong Kong and Taipei are among the B level, international hub cities. Hong Kong's city level score is 9, with 8 for agglomeration and 20 for connection degree, which shows that Hong Kong has a significant advantage in agglomeration degree and a weakness in connection degree. Among them, the number of soft agglomeration degree and hard agglomeration degree is 16 and 5 respectively, indicating that Hong Kong has more advantages in hard agglomeration; the ranking of soft connection and hard connection is 48 and 18 respectively, indicating that Hong Kong has disadvantages in soft connection. Taipei ranks 34 in the city level score, 18 in the degree of agglomeration and 49 in the degree of connection, indicating that Taipei has advantages in the degree of agglomeration, and has weakness in the degree of connection, among which the soft agglomeration and the hard agglomeration are 57 and 11, indicating that Taipei has more advantages in the hard agglomeration; of which the soft connection and the hard connection are 117 and 43, respectively. It can be seen that Taipei has a certain disadvantage in soft connection .
There are 22 Chinese cities have entered the international gateway city level, with 4 cities rank C+ level, namely Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Chengdu and Nanjing, with their city level scores ranking 40, 42, 59 and 60 respectively. Generally speaking, Chinese C+ level cities have more advantages in soft agglomeration. And there are 18 Chinese cities are ranked C level , including Hangzhou, Wuhan, Tianjin, Chongqing, Suzhou and Ningbo.etc. Hangzhou, Wuhan, Tianjin, Chongqing, Xi'an and Qingdao rank in the top 100 cities in the world, ranking 66, 69, 73, 76, 77 and 96 respectively. Most of the C level cities have advantages in soft agglomeration, and some cities have disadvantages in connection degree.
Overview of Chinese cities of C level and above
|
Level |
City |
Type of Agglomeration Degree - Connection Degree (AD-CD) |
Type of Hardness Degree - Softness Degree (HD-SD) |
|
A(1) |
Beijing |
High AD -High CD |
Strong HD- Strong SD |
|
B+(1) |
Shanghai |
Middle AD -Middle CD |
Middle HD- Strong SD |
|
B(2) |
Hong Kong |
High AD - Middle CD |
Middle HD- Strong SD |
|
|
Taipei |
Middle AD - Middle CD |
Middle HD- Middle SD |
|
C+(4) |
Guangzhou |
Middle AD - Middle CD |
Weak HD- Strong SD |
|
|
Shenzhen |
Middle AD - Middle CD |
Weak HD- Strong SD |
|
|
Chengdu |
Middle AD - Middle CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Nanjing |
Middle AD - Middle CD |
Weak HD- Strong SD |
|
C(18) |
Hangzhou |
Middle AD - Middle CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Wuhan |
Middle AD - Low CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Tianjin |
Middle AD - Low CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Chongqing |
Middle AD - Middle CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Suzhou |
Middle AD - Low CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Ningbo |
Middle AD - Low CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Xi'an |
Middle AD - Middle CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Qingdao |
Middle AD - Low CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Changsha |
Middle AD - Low CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Xiamen |
Middle AD - Low CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Hefei |
Middle AD - Low CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Dalian |
Middle AD - Low CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Shenyang |
Middle AD - Low CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Jinan |
Middle AD - Low CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Zhengzhou |
Middle AD - Low CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Kunming |
Middle AD - Low CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Harbin |
Middle AD - Low CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
|
|
Fuzhou |
Middle AD - Low CD |
Weak HD- Middle SD |
Chinese cities have some comparative advantages in the degree of agglomeration, and weakness in the degree of connection. Most cities in China belong to the type of low agglomeration -low connection, with a total number of 166, followed by the type of middle agglomeration -low connection, with a total number of 114. In terms of agglomeration degree, China has a certain comparative advantage in agglomeration degree. There are 2 cities with high agglomeration degree, and the number of cities with middle and low agglomeration degree are 123 and 166 respectively. On the whole, the number of middle agglomeration cities is almost the same as that of low agglomeration cities. In terms of connection degree, there is only 1 city ,Beijing, in China, with high connection, and the number of cities with middle connection and low connection is 10 and 280 respectively, which indicates that most cities in China are in a state of low connection, so it is urgent to improve their soft and hard connection.
Chinese cities need to strengthen both softness and hardness, but the weakness of hardness is more obvious. Most cities in China belong to the weak hardness - weak softness type, with a number of 192. In terms of hardness, China is at a certain disadvantage with only 1 city, Beijing, with strong hardness. The number of middle hardness and weak hardness cities is 3 and 287 respectively, which indicates that most cities in China have disadvantages in hardness. From the perspective of softness, the number of cities with middle softness is in a certain advantage. The number of cities with strong softness is 6, and the number of cities with middle softness and weak softness are 93 and 192, respectively. Compared with the hardness, the number of cities with middle softness is significantly more, but nearly 2 / 3 of the cities are still of the type of weak softness, indicating that the softness of most cities in China are weak, so it is urgent to improve their soft agglomeration and soft connection.
The report, for the first time, attempts to measure the implementation progress of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) from the perspective of Urban Sustainable Competitiveness(USC). The sustainable development goals of the United Nations are committed to eradicating poverty, protecting the earth and ensuring peace and prosperity for human beings through concerted action. It was put forward in September 2015 to guide member countries to thoroughly solve the development problems of society, economy and environment in an integrated way in the 15 years from 2015 to 2030, and move towards sustainable development.
The Sustainable Development Goals of the United Nations (SDGs), including 17 goals, 169 specific goals and 232 indicators, involve all aspects of economic, social and environmental development. They are interrelated and form a comprehensive organic target system. It is found that these goals are not one-dimensional related, but multi-dimensional related. The report creatively deconstructs the target system of SDGs, abstracts the core content of SDGs in the way of target matrix, and uses the indicator system of Urban Sustainable Competitiveness as a tool to monitor the progress of global cities in implementing the SDGs, especially the sustainable cities and communities (SDG11).
Through monitoring SDGs, the report found that almost all countries and cities have varying degrees of shortcomings in the implementation of SDGs. South America performed well in goals such as clean energy, sustainable production and consumption, and climate action but the rest are equal to or below the global average. Asian cities performed better than the world average in zero hunger, water and sanitation, underwater life, land life, and peace and justice while the rest performed at or below the global average. Most European cities are well above the global average in implementing the SDGs but they are facing significant challenges in climate action and sustainable consumption and production. North America as a whole is doing well, but its performance in climate action and peace and justice needs to be improved. Most indicators of SDGs for African cities are well below the world average, with only a few doing well.
Top20 Cities (SDGs)
|
City |
Country |
Ranking for SDGs |
City |
Country |
Ranking for SDGs |
|
New York |
United States |
1 |
Atlanta |
United States |
11 |
|
London |
United Kingdom |
2 |
Sydney |
Australia |
12 |
|
Tokyo |
Japan |
3 |
Chicago |
United States |
13 |
|
Paris |
France |
4 |
Seattle |
United States |
14 |
|
Singapore |
Singapore |
5 |
Dublin |
Ireland |
15 |
|
San Francisco |
United States |
6 |
Philadelphia |
United States |
16 |
|
Los Angeles |
United States |
7 |
Taipei |
China |
17 |
|
Boston |
United States |
8 |
Houston |
United States |
18 |
|
Dallas |
United States |
9 |
Copenhagen |
Denmark |
19 |
|
Amsterdam |
Netherlands |
10 |
Melbourne |
Australia |
20 |
Source: Global urban competitiveness database of CASS
Specifically, the top 20 cities in the world in terms of implementing the SDGs are: New York, London, Tokyo, Paris, Singapore, San Francisco, Los Angeles, Boston, Dallas, Amsterdam, Atlanta, Sydney, Chicago, Seattle, Dublin, Philadelphia, Taipei, Houston, Copenhagen, Melbourne. Half of them are in the United States, 5 in Europe, 3 in Asia and 2 in Oceania.
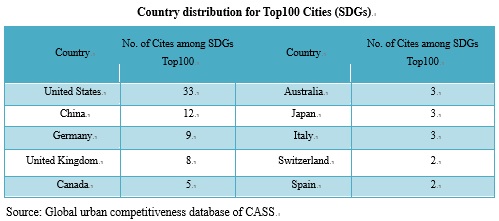
From the distribution of the top 100 cities, there are located in 29 countries, of which 33 are in the United States, with a high degree of concentration, 12 in China, 9 in Germany, 8 in the United Kingdom, 5 in Canada, 3 in Australia, 3 in Japan, 3 in Italy, 2 in Switzerland and 2 in Spain.

From the regional distribution of the top 200 cities, North America and Europe lead the world, occupying 68 seats and 67 seats respectively, followed by Asia, occupying 56 seats. Others are distributed in Oceania (6), South America (6) and Africa (1).

In the comprehensive ranking of SDGs, China has 1 city in the top 20, which is Taipei; 12 cities in the top 100, including Beijing, Shanghai, Chengdu, Hong Kong, Nanjing, Guangzhou, Xi'an, Shenzhen, Hangzhou, Chongqing and Wuhan.
Cities play an increasingly important role in economic and social development. In the process of rapid urbanization, sustainable development of cities has become one of the most important issues. Therefore, item 11 of the SDGs proposes "Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable". Sustainable Development Goal 11 (SDG11) is a concentrated display of sustainable development in the city.
Deconstructing SDG11 in a similar way of target matrix and monitoring it we found: housing burden, social equity, heritage protection, production and consumption mode, social security, etc. are the common short boards of urban sustainable development goals. The overall performance of Europe and North America is relatively outstanding, but the development between cities is unbalanced, and most cities also have short boards. Living burden in South America is heavy and the security situation needs to be improved. The progress coexist with the deterioration of problems in Asia cities, and the sustainable development of African cities lags behind in an all-round way.

In terms of ranking, the top 20 cities in implementing sdg11 are: Tokyo, London, Rome, Paris, New York, Hong Kong, Singapore, Seattle, Melbourne, Boston, Philadelphia, Sydney, Stockholm, Osaka, Seoul, Los Angeles, Stuttgart, San Francisco, Hiroshima and Barcelona. The United States has 6 cities, Japan has 3 cities, Australia has 2 cities and the rest 9 countries have 1 city respectively.

From the national distribution of the top 100 cities, 27 countries are involved, but 80 cities are distributed within 10 countries. Among them, there are 24 in the United States, 12 in Germany ,12 in China, 6 in the United Kingdom, 6 in Japan, 5 in Italy, 4 in Canada, 2 in Australia, 2 in Spain and 2 in Israel.

In terms of the regional distribution of the top 200 cities, Europe is the first, occupying 63 seats, North America is the second, occupying 62 seats, Asia is the third, occupying 58 seats. Others are distributed in South America (9), Oceania (5), and Africa (3).

In the global ranking of SDG11, China has 1 city in the top 20, which is Hong Kong; 12 cities in the top 100, including Taipei, Shenzhen, Nanjing, Tainan, Xiamen, Shanghai, Beijing, Taichung, Wuhan, Shenyang and Suzhou.
This report is the fourth Annual Report on Global Urban Competitiveness, jointly launched by the The Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (National Academy of Economic Strategy) and UN-HABITAT. Using the indicator system and objective data, the report provides a detailed assessment of the competitiveness of 1,006 cities. The report measures the development pattern of global urban competitiveness as a whole and discusses important theoretical and practical issues in global urban development. The report has important reference significance and research value for global urban government departments, domestic and foreign enterprises, relevant research institutions, and the public.
Appendix:
Top200 Cities for Economic Competitiveness (2019-2020)
|
City Name |
Country |
Rank |
City Name |
Country |
Rank |
|
New York-Newark |
USA |
1 |
Montreal |
Canada |
101 |
|
London |
United Kingdom |
2 |
Jakarta |
Indonesia |
102 |
|
Singapore |
Singapore |
3 |
Nagoya |
Japan |
103 |
|
Shenzhen |
China |
4 |
Dongguan |
China |
104 |
|
San Jose |
USA |
5 |
San Antonio |
USA |
105 |
|
Tokyo |
Japan |
6 |
Hiroshima |
Japan |
106 |
|
San Francisco-Oakland |
USA |
7 |
Oslo |
Norway |
107 |
|
Munich |
Germany |
8 |
Dresden |
Germany |
108 |
|
Los Angeles-Long Beach-Santa Ana |
USA |
9 |
Hague |
Netherlands |
109 |
|
Shanghai |
China |
10 |
Indianapolis |
USA |
110 |
|
Dallas-Fort Worth |
USA |
11 |
Provo-Orem |
USA |
111 |
|
Houston |
USA |
12 |
Hamilton |
Canada |
112 |
|
Hong Kong |
China |
13 |
Macao |
China |
113 |
|
Dublin |
Ireland |
14 |
Gold Coast |
Australia |
114 |
|
Seoul |
Republic of Korea |
15 |
Kansas City |
USA |
115 |
|
Boston |
USA |
16 |
Leipzig |
Germany |
116 |
|
Beijing |
China |
17 |
Virginia Beach |
USA |
117 |
|
Guangzhou |
China |
18 |
Jedda |
Saudi Arabia |
118 |
|
Miami |
USA |
19 |
Bangkok |
Thailand |
119 |
|
Chicago |
USA |
20 |
Brisbane |
Australia |
120 |
|
Paris |
France |
21 |
Nantong |
China |
121 |
|
Frankfurt am Main |
Germany |
22 |
Pittsburgh |
USA |
122 |
|
Tel Aviv-Yafo |
Israel |
23 |
Melbourne |
Australia |
123 |
|
Seattle |
USA |
24 |
Helsinki |
Finland |
124 |
|
Suzhou |
China |
25 |
Madrid |
Spain |
125 |
|
Stockholm |
Sweden |
26 |
Kaohsiung |
China |
126 |
|
Philadelphia |
USA |
27 |
Charleston-North Charleston |
USA |
127 |
|
Stuttgart |
Germany |
28 |
Mexico City |
Mexico |
128 |
|
Osaka |
Japan |
29 |
Hartford |
USA |
129 |
|
Toronto |
Canada |
30 |
Ottawa-Gatineau |
Canada |
130 |
|
Baltimore |
USA |
31 |
Incheon |
Republic of Korea |
131 |
|
Bridgeport-Stamford |
USA |
32 |
Sapporo |
Japan |
132 |
|
Dusseldorf |
Germany |
33 |
Riverside-San Bernardino |
USA |
133 |
|
San Diego(US) |
USA |
34 |
Bristol |
United Kingdom |
134 |
|
Geneva |
Switzerland |
35 |
Gothenburg |
Sweden |
135 |
|
Atlanta |
USA |
36 |
Allentown |
USA |
136 |
|
Cleveland |
USA |
37 |
Rome |
Italy |
137 |
|
Perth |
Australia |
38 |
Colorado Springs |
USA |
138 |
|
Denver-Aurora |
USA |
39 |
Grand Rapids |
USA |
139 |
|
Detroit |
USA |
40 |
Lille |
France |
140 |
|
Istanbul |
Turkey |
41 |
jinan |
China |
141 |
|
Nanjing |
China |
42 |
Kitakyushu-Fukuoka |
Japan |
142 |
|
Wuhan |
China |
43 |
Milan |
Italy |
143 |
|
Taipei |
China |
44 |
Providence |
USA |
144 |
|
Charlotte |
USA |
45 |
Hefei |
China |
145 |
|
Nashville-Davidson |
USA |
46 |
Lyon |
France |
146 |
|
Minneapolis-Saint Paul |
USA |
47 |
Samut Prakan |
Thailand |
147 |
|
Berlin |
Germany |
48 |
Quanzhou |
China |
148 |
|
Austin |
USA |
49 |
Xiamen |
China |
149 |
|
Hamburg |
Germany |
50 |
Xi'an |
China |
150 |
|
Vienna |
Austria |
51 |
Edmonton |
Canada |
151 |
|
Abu Dhabi |
United Arab Emirates |
52 |
Rotterdam |
Netherlands |
152 |
|
Raleigh |
USA |
53 |
Fuzhou(FJ) |
China |
153 |
|
Chengdu |
China |
54 |
Birmingham(US) |
USA |
154 |
|
Cologne |
Germany |
55 |
Honolulu |
USA |
155 |
|
Las Vegas |
USA |
56 |
Santiago de Chile |
Chile |
156 |
|
Zurich |
Switzerland |
57 |
Columbia |
USA |
157 |
|
Salt Lake City |
USA |
58 |
West Yorkshire |
United Kingdom |
158 |
|
Richmond |
USA |
59 |
Worcester |
USA |
159 |
|
Copenhagen |
Denmark |
60 |
Dayton |
USA |
160 |
|
Orlando |
USA |
61 |
Delhi |
India |
161 |
|
Moscow |
Russian Federation |
62 |
San Jose |
Costa Rica |
162 |
|
Sydney |
Australia |
63 |
Yangzhou |
China |
163 |
|
Hangzhou |
China |
64 |
Auckland |
New Zealand |
164 |
|
Wuxi |
China |
65 |
Cape Coral |
USA |
165 |
|
Barcelona |
Spain |
66 |
Valencia |
Spain |
166 |
|
Birmingham |
United Kingdom |
67 |
Lima |
Peru |
167 |
|
Changsha |
China |
68 |
Akron |
USA |
168 |
|
Milwaukee |
USA |
69 |
Bogota |
Colombia |
169 |
|
Vancouver |
Canada |
70 |
Liverpool |
United Kingdom |
170 |
|
Brussels |
Belgium |
71 |
Medina |
Saudi Arabia |
171 |
|
Dubai |
United Arab Emirates |
72 |
Knoxville |
USA |
172 |
|
Calgary |
Canada |
73 |
Zhuhai |
China |
173 |
|
Doha |
Qatar |
74 |
Zhenjiang |
China |
174 |
|
Hannover |
Germany |
75 |
Yantai |
China |
175 |
|
Qingdao |
China |
76 |
Marseille-Aix-en-Provence |
France |
176 |
|
Columbus |
USA |
77 |
Sheffield |
United Kingdom |
177 |
|
Sendai |
Japan |
78 |
Jerusalem |
Israel |
178 |
|
Louisville |
USA |
79 |
Belfast |
United Kingdom |
179 |
|
Essen |
Germany |
80 |
Taizhou(js) |
China |
180 |
|
Chongqing |
China |
81 |
Panama City |
Panama |
181 |
|
Tianjin |
China |
82 |
Bucuresti |
Romania |
182 |
|
Kuala Lumpur |
Malaysia |
83 |
Venice |
Italy |
183 |
|
Foshan |
China |
84 |
Sacramento |
USA |
184 |
|
Washington, D.C. |
USA |
85 |
Dalian |
China |
185 |
|
Ulsan |
Republic of Korea |
86 |
Glasgow |
United Kingdom |
186 |
|
Oklahoma City |
USA |
87 |
Buffalo |
USA |
187 |
|
Manchester |
United Kingdom |
88 |
Manila |
Philippines |
188 |
|
Riyadh |
Saudi Arabia |
89 |
Mecca |
Saudi Arabia |
189 |
|
Ningbo |
China |
90 |
New Haven |
USA |
190 |
|
Phoenix-Mesa |
USA |
91 |
Xuzhou |
China |
191 |
|
Antwerp |
Belgium |
92 |
Busan |
Republic of Korea |
192 |
|
Amsterdam |
Netherlands |
93 |
Warsaw |
Poland |
193 |
|
Zhengzhou |
China |
94 |
Ogden |
USA |
194 |
|
Tampa-St. Petersburg |
USA |
95 |
Changwon |
Republic of Korea |
195 |
|
Baton Rouge |
USA |
96 |
Buenos Aires |
Argentina |
196 |
|
Cincinnati |
USA |
97 |
Nanchang |
China |
197 |
|
Dortmund |
Germany |
98 |
Gwangju |
Republic of Korea |
198 |
|
Changzhou |
China |
99 |
Daejeon |
Republic of Korea |
199 |
|
Haifa |
Israel |
100 |
Shenyang |
China |
200 |
Top200 Cities for Sustainable Competitiveness (2019-2020)
|
City Name |
Country |
Rank |
City Name |
Country |
Rank |
|
Singapore |
Singapore |
1 |
Malaga |
Spain |
101 |
|
Tokyo |
Japan |
2 |
Athens |
Greece |
102 |
|
New York-Newark |
USA |
3 |
Wuxi |
China |
103 |
|
London |
United Kingdom |
4 |
Dortmund |
Germany |
104 |
|
San Francisco-Oakland |
USA |
5 |
Louisville |
USA |
105 |
|
Paris |
France |
6 |
Pretoria |
South Africa |
106 |
|
Hong Kong |
China |
7 |
Essen |
Germany |
107 |
|
Osaka |
Japan |
8 |
Tianjin |
China |
108 |
|
Los Angeles-Long Beach-Santa Ana |
USA |
9 |
Foshan |
China |
109 |
|
Chicago |
USA |
10 |
Taichung |
China |
110 |
|
Barcelona |
Spain |
11 |
Brisbane |
Australia |
111 |
|
Moscow |
Russian Federation |
12 |
Auckland |
New Zealand |
112 |
|
Stockholm |
Sweden |
13 |
Dresden |
Germany |
113 |
|
Seoul |
Republic of Korea |
14 |
Saint Petersburg |
Russian Federation |
114 |
|
Munich |
Germany |
15 |
Virginia Beach |
USA |
115 |
|
Stuttgart |
Germany |
16 |
Calgary |
Canada |
116 |
|
Boston |
USA |
17 |
Las Vegas |
USA |
117 |
|
Madrid |
Spain |
18 |
Bogota |
Colombia |
118 |
|
Shenzhen |
China |
19 |
San Jose |
USA |
119 |
|
Frankfurt am Main |
Germany |
20 |
Medina |
Saudi Arabia |
120 |
|
Philadelphia |
USA |
21 |
Dongguan |
China |
121 |
|
Toronto |
Canada |
22 |
Wuhan |
China |
122 |
|
Taipei |
China |
23 |
Lima |
Peru |
123 |
|
Houston |
USA |
24 |
Kaohsiung |
China |
124 |
|
Miami |
USA |
25 |
Dusseldorf |
Germany |
125 |
|
Berlin |
Germany |
26 |
Tampa-St. Petersburg |
USA |
126 |
|
Melbourne |
Australia |
27 |
Belfast |
United Kingdom |
127 |
|
Rome |
Italy |
28 |
Jedda |
Saudi Arabia |
128 |
|
Shanghai |
China |
29 |
Worcester |
USA |
129 |
|
Seattle |
USA |
30 |
Hangzhou |
China |
130 |
|
Manchester |
United Kingdom |
31 |
Lyon |
France |
131 |
|
Atlanta |
USA |
32 |
New Haven |
USA |
132 |
|
San Jose |
USA |
33 |
Leipzig |
Germany |
133 |
|
Cleveland |
USA |
34 |
Dublin |
Ireland |
134 |
|
Sydney |
Australia |
35 |
Hamilton |
Canada |
135 |
|
Hiroshima |
Japan |
36 |
Hague |
Netherlands |
136 |
|
Birmingham |
United Kingdom |
37 |
Buffalo |
USA |
137 |
|
Beijing |
China |
38 |
Charlotte |
USA |
138 |
|
Milan |
Italy |
39 |
Liege |
Belgium |
139 |
|
Montreal |
Canada |
40 |
Zaragoza |
Spain |
140 |
|
Dallas-Fort Worth |
USA |
41 |
Torino |
Italy |
141 |
|
Buenos Aires |
Argentina |
42 |
Colorado Springs |
USA |
142 |
|
Vienna |
Austria |
43 |
Chengdu |
China |
143 |
|
Tel Aviv-Yafo |
Israel |
44 |
Qingdao |
China |
144 |
|
Denver-Aurora |
USA |
45 |
Nashville-Davidson |
USA |
145 |
|
Hamburg |
Germany |
46 |
Macao |
China |
146 |
|
Zurich |
Switzerland |
47 |
Rio de Janeiro |
Brazil |
147 |
|
Nagoya |
Japan |
48 |
San Antonio |
USA |
148 |
|
Kitakyushu-Fukuoka |
Japan |
49 |
Zhongshan |
China |
149 |
|
Baltimore |
USA |
50 |
Minneapolis-Saint Paul |
USA |
150 |
|
Copenhagen |
Denmark |
51 |
Sendai |
Japan |
151 |
|
Hannover |
Germany |
52 |
Lisbon |
Portugal |
152 |
|
Salt Lake City |
USA |
53 |
Oslo |
Norway |
153 |
|
San Diego(US) |
USA |
54 |
Ningbo |
China |
154 |
|
Perth |
Australia |
55 |
Lille |
France |
155 |
|
Washington, D.C. |
USA |
56 |
Liverpool |
United Kingdom |
156 |
|
Incheon |
Republic of Korea |
57 |
Provo-Orem |
USA |
157 |
|
Suzhou |
China |
58 |
Changzhou |
China |
158 |
|
Raleigh |
USA |
59 |
Zhengzhou |
China |
159 |
|
Kuala Lumpur |
Malaysia |
60 |
Amman |
Jordan |
160 |
|
Vancouver |
Canada |
61 |
Venice |
Italy |
161 |
|
Amsterdam |
Netherlands |
62 |
Dammam |
Saudi Arabia |
162 |
|
Astana |
Kazakhstan |
63 |
Rotterdam |
Netherlands |
163 |
|
Geneva |
Switzerland |
64 |
Tainan |
China |
164 |
|
Brussels |
Belgium |
65 |
Changsha |
China |
165 |
|
Detroit |
USA |
66 |
Leicester |
United Kingdom |
166 |
|
Guangzhou |
China |
67 |
Tehran |
Islamic Republic of Iran |
167 |
|
Austin |
USA |
68 |
San Juan |
Puerto Rico |
168 |
|
Orlando |
USA |
69 |
Providence |
USA |
169 |
|
West Yorkshire |
United Kingdom |
70 |
Shizuoka-Hamamatsu |
Japan |
170 |
|
Cologne |
Germany |
71 |
Verona |
Italy |
171 |
|
Helsinki |
Finland |
72 |
Johannesburg |
South Africa |
172 |
|
Daejeon |
Republic of Korea |
73 |
Baton Rouge |
USA |
173 |
|
Istanbul |
Turkey |
74 |
Bangkok |
Thailand |
174 |
|
Ulsan |
Republic of Korea |
75 |
New Orleans |
USA |
175 |
|
Richmond |
USA |
76 |
Gold Coast |
Australia |
176 |
|
Valencia |
Spain |
77 |
Ottawa-Gatineau |
Canada |
177 |
|
Jerusalem |
Israel |
78 |
Bologna |
Italy |
178 |
|
Columbus |
USA |
79 |
Leon |
Mexico |
179 |
|
Sao Paulo |
Brazil |
80 |
Sofia |
Bulgaria |
180 |
|
Bridgeport-Stamford |
USA |
81 |
Indianapolis |
USA |
181 |
|
Phoenix-Mesa |
USA |
82 |
Shenyang |
China |
182 |
|
Nanjing |
China |
83 |
Pittsburgh |
USA |
183 |
|
Doha |
Qatar |
84 |
Ogden |
USA |
184 |
|
Haifa |
Israel |
85 |
Florence |
Italy |
185 |
|
Mexico City |
Mexico |
86 |
Kansas City |
USA |
186 |
|
Antwerp |
Belgium |
87 |
Budapest |
Hungary |
187 |
|
Hartford |
USA |
88 |
Montevideo |
Uruguay |
188 |
|
Riyadh |
Saudi Arabia |
89 |
Zhuhai |
China |
189 |
|
Sapporo |
Japan |
90 |
Honolulu |
USA |
190 |
|
Gwangju |
Republic of Korea |
91 |
Barcelona-Puerto La Cruz |
Venezuela |
191 |
|
Busan |
Republic of Korea |
92 |
Oklahoma City |
USA |
192 |
|
Naples |
Italy |
93 |
Dalian |
China |
193 |
|
Xiamen |
China |
94 |
Minsk |
Belarus |
194 |
|
Milwaukee |
USA |
95 |
Porto |
Portugal |
195 |
|
Glasgow |
United Kingdom |
96 |
Mecca |
Saudi Arabia |
196 |
|
Adelaide |
Australia |
97 |
Xi'an |
China |
197 |
|
Dubai |
United Arab Emirates |
98 |
Ahvaz |
Islamic Republic of Iran |
198 |
|
Daegu |
Republic of Korea |
99 |
Hefei |
China |
199 |
|
Santiago de Chile |
Chile |
100 |
Marseille-Aix-en-Provence |
France |
200 |
Global Urban Classification 2019-2020(A/B/C level)
|
City level |
City |
Country |
City level |
City |
Country |
|
A+ |
New York-Newark |
USA |
C |
Doha |
Qatar |
|
A+ |
London |
United Kingdom |
C |
Lyon |
France |
|
A+ |
Tokyo |
Japan |
C |
Sofia |
Bulgaria |
|
A |
Beijing |
China |
C |
Columbia |
USA |
|
A |
Paris |
France |
C |
Brisbane |
Australia |
|
B+ |
Seoul |
Republic of Korea |
C |
Phoenix-Mesa |
USA |
|
B+ |
Shanghai |
China |
C |
Birmingham |
United Kingdom |
|
B+ |
Chicago |
USA |
C |
Pittsburgh |
USA |
|
B |
Hong Kong |
China |
C |
Calgary |
Canada |
|
B |
Moscow |
Russian Federation |
C |
Bangalore |
India |
|
B |
Singapore |
Singapore |
C |
Bologna |
Italy |
|
B |
Madrid |
Spain |
C |
Riyadh |
Saudi Arabia |
|
B |
Boston |
USA |
C |
Baltimore |
USA |
|
B |
Los Angeles-Long Beach-Santa Ana |
USA |
C |
Orlando |
USA |
|
B |
Istanbul |
Turkey |
C |
Johannesburg |
South Africa |
|
B |
Toronto |
Canada |
C |
Ankara |
Turkey |
|
B |
Milan |
Italy |
C |
Qingdao |
China |
|
B |
Amsterdam |
Netherlands |
C |
Rio de Janeiro |
Brazil |
|
B |
Houston |
USA |
C |
Lima |
Peru |
|
B |
San Francisco-Oakland |
USA |
C |
Columbus |
USA |
|
B |
Sydney |
Australia |
C |
Cleveland |
USA |
|
B |
Stockholm |
Sweden |
C |
San Jose |
USA |
|
B |
Atlanta |
USA |
C |
Changsha |
China |
|
B |
Sao Paulo |
Brazil |
C |
Dusseldorf |
Germany |
|
B |
Brussels |
Belgium |
C |
Cairo |
Egypt |
|
B |
Dallas-Fort Worth |
USA |
C |
Porto |
Portugal |
|
B |
Munich |
Germany |
C |
Santiago de Chile |
USA |
|
B |
Rome |
Italy |
C |
Bristol |
United Kingdom |
|
B |
Dublin |
Ireland |
C |
Xiamen |
China |
|
B |
Barcelona |
Spain |
C |
Cincinnati |
USA |
|
B |
Vienna |
Austria |
C |
Hannover |
Germany |
|
B |
Osaka |
Japan |
C |
Glasgow |
United Kingdom |
|
B |
Berlin |
Germany |
C |
Hefei |
China |
|
B |
Taipei |
China |
C |
Zagreb |
Croatia |
|
C+ |
Zurich |
Switzerland |
C |
Naples |
Italy |
|
C+ |
Bangkok |
Thailand |
C |
Belgrade |
Serbia |
|
C+ |
Melbourne |
Australia |
C |
Nashville-Davidson |
USA |
|
C+ |
Seattle |
USA |
C |
Dalian |
China |
|
C+ |
Copenhagen |
Denmark |
C |
Ottawa-Gatineau |
Canada |
|
C+ |
Guangzhou |
China |
C |
Abu Dhabi |
United Arab Emirates |
|
C+ |
Dubai |
United Arab Emirates |
C |
Valencia |
Spain |
|
C+ |
Shenzhen |
China |
C |
Adelaide |
Australia |
|
C+ |
Mumbai |
India |
C |
Shenyang |
China |
|
C+ |
Washington, D.C. |
USA |
C |
Salt Lake City |
USA |
|
C+ |
Athens |
Greece |
C |
Tampa-St. Petersburg |
USA |
|
C+ |
Philadelphia |
USA |
C |
Chennai |
India |
|
C+ |
Warsaw |
Poland |
C |
Rochester |
USA |
|
C+ |
Helsinki |
Finland |
C |
Marseille-Aix-en-Provence |
France |
|
C+ |
Prague |
Czech Republic |
C |
Hyderabad |
India |
|
C+ |
Frankfurt am Main |
Germany |
C |
Las Vegas |
USA |
|
C+ |
Montreal |
Canada |
C |
jinan |
China |
|
C+ |
Bogota |
Colombia |
C |
San Diego(US) |
USA |
|
C+ |
Denver-Aurora |
USA |
C |
Indianapolis |
USA |
|
C+ |
Hamburg |
Germany |
C |
Edmonton |
Canada |
|
C+ |
Kuala Lumpur |
Malaysia |
C |
Zhengzhou |
China |
|
C+ |
Miami |
USA |
C |
Rotterdam |
Netherlands |
|
C+ |
Buenos Aires |
Argentina |
C |
Nagoya |
Japan |
|
C+ |
Oslo |
Norway |
C |
Cape Town |
South Africa |
|
C+ |
Chengdu |
China |
C |
Kunming |
China |
|
C+ |
Nanjing |
China |
C |
Bucuresti |
Romania |
|
C+ |
Minneapolis-Saint Paul |
USA |
C |
Toulouse |
France |
|
C+ |
Auckland |
New Zealand |
C |
Perth |
Australia |
|
C+ |
Budapest |
Hungary |
C |
Portland |
USA |
|
C |
Lisbon |
Portugal |
C |
Suzhou |
China |
|
C |
Mexico City |
Mexico |
C |
Liverpool |
United Kingdom |
|
C |
Hangzhou |
China |
C |
Pune |
India |
|
C |
Manchester |
United Kingdom |
C |
Krakow |
Poland |
|
C |
Vancouver |
Canada |
C |
Riga |
Latvia |
|
C |
Wuhan |
China |
C |
Incheon |
Republic of Korea |
|
C |
Stuttgart |
Germany |
C |
San Antonio |
USA |
|
C |
Jakarta |
Indonesia |
C |
Harbin |
China |
|
C |
Geneva |
Switzerland |
C |
Nairobi |
Kenya |
|
C |
Tianjin |
China |
C |
Fuzhou |
China |
|
C |
Charlotte |
USA |
C |
Casablanca |
Morocco |
|
C |
Delhi |
India |
C |
Ningbo |
China |
|
C |
Chongqing |
China |
C |
Bordeaux |
France |
|
C |
Xi'an |
China |
C |
Tucson |
USA |
|
C |
Detroit |
USA |
C |
Kiev |
Ukraine |
|
C |
Austin |
USA |
C |
Richmond |
USA |
|
|
|
|
C |
Raleigh |
USA |
